Providing E-Learning Using Content Delivery Networks
 Associations Now
Associations Now
Members want to be able to quickly access your content anytime and anywhere. Scitent eLearning CEO Deb McMahon and Director of IT and Product Development Laurent Jean-Marius explain how content delivery networks can make that happen.
What is a content delivery network?
CDNs are systems of distributed servers that play an important role in delivering fast and efficient internet experiences. Specifically, they provide faster content delivery by replicating the content throughout the system so it exists in many places at once. Members access a copy of the data near their location, as opposed to all members accessing the same central server.
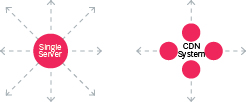
Why would an association want to use CDNs for e-learning content?
Frustrations happen fast in the online world, especially on mobile devices. This means an association’s e-learning content must be optimized for speed, and a CDN helps ensure this. Ultimately, this will improve a member’s interaction with association content, positively impacting an association’s brand reputation and potentially attracting new members.
Because online courses are mainly composed of static content such as images, videos, and audio clips, they are excellent candidates to be deployed on a CDN. Associations can explore CDN options with their online course providers.
What are their operational, technological, and business benefits?
Because of the distributed nature of a CDN, it offers high availability and redundancy of service on multiple nodes all over the world, meaning no downtimes. And it offloads the traffic from an association’s current servers and automatically scales up based on the traffic, offering infrastructure and IT cost savings. Associations that use CDNs don’t have to worry about sizing up server space, no matter how many new members and learners are added.
Finally, CDNs are typically more secure than other configurations. Because a CDN acts as a cache—only consuming static content—information from an association’s database is less vulnerable to security threats. In fact, many CDNs auto-detect threats and actively filter common security issues.
[This article was originally published in the Associations Now print edition, titled "Speedy Delivery."]

